
We look at evidence in relation to Large Language Models (LLMs)
In a digital context, evidence refers to any information that is used to support or refute a claim. Evidence is closely linked to the observation of events and the determination of facts. In any situation, evidence serves as the means by which we establish what happened, and what is true. The process of gathering evidence involves observing events and collecting data that can be used to support or refute a particular claim.
As generative AI becomes increasingly prevalent, the importance of digital evidence is set to skyrocket. In a world where it’s difficult to discern what’s true if it’s generated, the value of evidence that’s closely related to reality will become crucial and highly valuable. While some applications like fiction, movie scripts, and game plots don’t necessarily require a strong relationship to reality, the same cannot be said for applications with high real-world consequences. Investing millions of dollars based on generated statements simply won’t cut it.
To address this, we can harness the power of Transformers and LLMs, but we must combine them with other robust and explainable AI (XAI) techniques that operate in real-time to capture data as close as possible to the original source. This type of reality capture setup can also be used for reinforcement learning without human involvement.
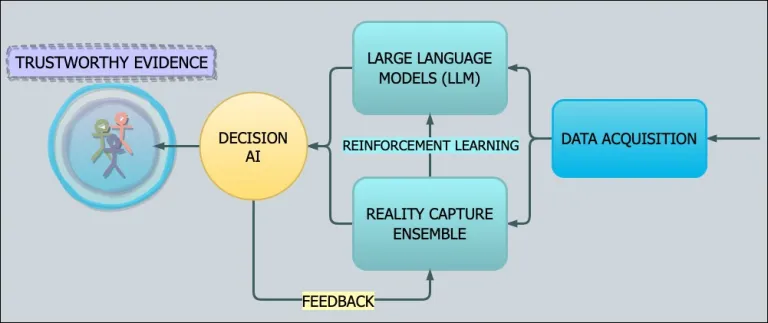
In the picture above, a large language model featuring generative AI is extracting information from unstructured data. It works side–by–side with an AI ensemble (multiple models) to robustly capture perspectives in the data. Outputs from both models are compared to see if they agree. If not, the AI ensemble is used instead of the LLM (which may be hallucinating) and feedback can be passed to the LLM.
The purpose of evidence gathering is to gain a complete understanding of the events in a given situation and to establish the facts of the case. This process can be challenging and involves analyzing all available information, which can be done using AI models capable of computing, analyzing, and evaluating different perspectives in data. These models differ from generative AI models because they must provide detailed explanations of everything, from algorithm insights to data sources, authority, references, data sample rate, and more. In essence, it is absolutely crucial to use AI models that offer complete transparency and accountability, allowing for thorough understanding and interpretation of the data.
In summary, evidence in a digital context refers to any information used to support or refute a claim that is produced electronically. This information can be in various forms, and it is often at least partly unstructured data. Advanced technologies like LLMs, NLP and other AI models can be used to extract valuable insights from this data, but it needs to be collected, stored, and analyzed in a way that maintains its authenticity, integrity and transparency.